Research and Development sub-projects
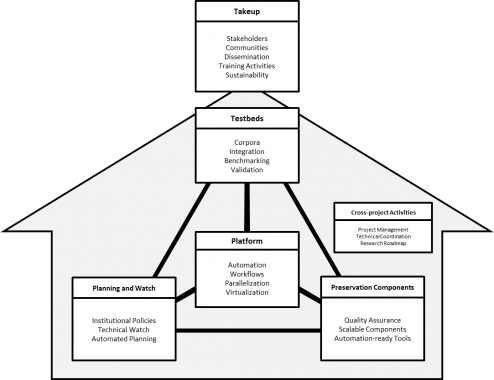
SCAPE approached digital preservation through following research and development sub-projects: Testbeds, Preservation Components, Platform, and Planning and Watch.
The SCAPE Testbeds were the primary driver for the rest of the project, in that they defined use case scenarios (SCAPE Stories), created preservation workflows, and assessed the large scale applicability of the SCAPE Preservation Platform and the preservation components developed within the project. Using these software components, test environments were created for the different scenarios and the complex large scale preservation workflows.
SCAPE Preservation Components addressed known limitations of digital preservation systems on three levels:
- scalability
- functional coverage
- quality
This sub-project improved and extended existing tools, developed new ones where necessary, and applied proven approaches to the problem of ensuring quality in digital preservation (SCAPE Tools).
Building on the state of the art and focusing on formats and tools which were considered most important by the Testbeds sub-project, SCAPE investigated methods to parallelise and embed components in robust and scalable workflows. A major focus was the ability to capture relevant provenance and contextual information and metadata, and to provide usable outputs for automated policy-driven preservation.
The SCAPE Platform provided an extensible infrastructure for the execution of digital preservation processes on large volumes of data. It includes a flexible mechanism for the integration of existing digital repository systems and provides a reference implementation. The Preservation Platform provided the underlying environment for large-scale testing and evaluation performed by the Testbeds and the Preservation Component providers in the project. The computational layer of the Preservation Platform system makes use of Hadoop, with the underlying distributed storage layer being based on HBase, which provides high performance and scalable data storage on top of Hadoop’s Distributed File System (HDFS).
The Planning and Watch Components developed in SCAPE address the bottleneck of decision processes and processing information required for decision making. Work on these components started with a conceptual analysis, based on extensive real-world application experience. A set of essential policy elements was defined and modelled. These elements make use of the SCAPE Policy Catalogue. Building on SCAPE’s machine-understandable policy representation and the first release of the automated planning component, core watch services were implemented. In the final phase the policy-aware planning component Plato has been fully integrated with the platform and repository operations.
Cross-project and Take-up Activities in SCAPE
The Cross-project Activities in SCAPE included project management and coordination as well as the investigation of Open Research Challenges and Future Research Challenges. These activities provided administrative control and technical coordination for the project as well as focused research on innovative and emerging technologies.
The project’s Take-up Activities aimed to provide both coordination for communication and dissemination of project results within and beyond the project. A number of training activities, which also incorporated Best Practice guidelines, aimed at fostering the take-up of project outputs at technical, operational and strategic levels. Furthermore, they ensure that SCAPE has a long-term and sustained impact beyond the runtime of the project.